What is staff turnover rate?
Staff turnover rate, also known as employee turnover rate or employment turnover rate, measures how frequently employees leave and are replaced within a company. Turnover can be categorized into two main types of departures.
- Voluntary turnover: When employees leave by choice, often for better opportunities, personal reasons, or dissatisfaction with their current role.
- Involuntary turnover: When employees are let go due to layoffs, furloughs, performance issues, or other company decisions.
Why turnover matters
High turnover rates can be costly and disruptive. They lead to increased recruitment and training expenses, lower employee morale, and potentially loss of valuable skills and knowledge. Conversely, a low turnover rate can indicate a stable and satisfied workforce, which benefits long-term organizational success.
Calculating employee turnover rate
To calculate turnover rate, use the following formula:
Divide the number of employees who left during a specific period by the average number of employees at the beginning and end of that period and multiply by 100.
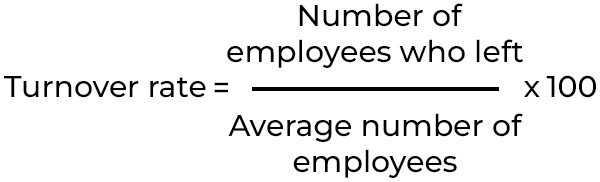
For example, if a company had 5,000 employees at the start of the year and 4,500 at the end, and 500 employees left during the year, the average number of employees would be 4,750. The turnover rate would be:
500 ÷ 4,750 × 100 = 10.53% turnover rate.
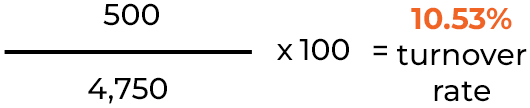
Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating employee turnover rate:
- Determine the period: Decide the time frame for which you want to calculate the turnover rate, typically a year.
- Count departures: Count the number of employees who left the company during this period.
- Average number of employees: Calculate the average number of employees during the same period. This can be done by adding the number of employees at the beginning and end of the period and dividing by two.
- Apply the formula: Divide the number of employees who left by the average number of employees, then multiply by 100 to get the turnover rate as a percentage.
Using turnover data
Understanding your turnover rate can help identify underlying issues within the organization. For instance, a high voluntary turnover rate might indicate problems with job satisfaction, management practices, or workplace culture. Addressing these issues can improve employee retention and overall organizational performance.
Why early employee recognition matters
BI WORLDWIDE Canada (BIW) emphasizes the significant impact of employee recognition and rewards on turnover rates. Our research shows that employees who are recognized are less likely to leave. For example, turnover is 4x higher among employees with low recognition rates compared to those who are frequently recognized. Employee recognition programs, such as DayMaker, can effectively reduce turnover by acknowledging and rewarding employees’ efforts and achievements.
Additionally, BIW highlights the importance of early recognition. Recognizing new employees early in their tenure can significantly reduce turnover within the first six months. This approach helps new hires feel valued and integrated into the company culture, increasing their likelihood of staying long-term.
The WorkHappier Profile tool uses employee engagement data to predict potential turnover, allowing companies to proactively address issues before they lead to resignations. This predictive approach helps organizations retain their best talent by identifying and mitigating factors that contribute to employee dissatisfaction.
By regularly monitoring and analyzing turnover rates and implementing effective recognition and engagement strategies, companies can develop a more stable and productive workforce.
Bottom line
Frequent and early recognition are critical strategies for reducing turnover. By implementing effective recognition programs and using predictive tools to address potential issues, companies can create a more stable and motivated workforce, ultimately driving long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes, high turnover is often considered a red flag. It can indicate underlying issues such as poor management, lack of career development opportunities, or a toxic work environment.
A 20% staff turnover rate is generally considered high and may indicate issues within the organization that need to be addressed.
A 20% turnover rate means that 20% of the workforce left the company within the specified period. This can signal potential problems with employee satisfaction or retention strategies.
A 10% employee turnover rate indicates that 10% of the employees left the company during the given period. This rate is often seen as more manageable and may be closer to industry averages.
A good employee turnover ratio varies by industry, but generally, a rate below 10 is considered good.
